Rewrite an Existing Magento 2 Controller
This article will help you understand how to rewrite an existing Magento 2 controller.
Similar to how blocks, helpers and models are rewritten, we can create our own module and add a preference within in the module’s di.xml file.
This article will show an example of how to override the Magento\Cms\Controller\Index\Index controller class. For simplicity, the example below will simply add a success message onto the home page to confirm the controller has been rewritten successfully.
If you don’t have a custom module structure set up, create one by starting with the module.xml file.
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<config xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="../../../../../lib/internal/Magento/Framework/Module/etc/module.xsd">
<module name="Siphor_Custom" setup_version="0.0.1" />
</config>
Register the custom module by adding a registration.php file.
<?php
\Magento\Framework\Component\ComponentRegistrar::register(
\Magento\Framework\Component\ComponentRegistrar::MODULE,
'Siphor_Custom',
__DIR__
);
Run the command to enable the module from within the Magento root directory.
$ /path/to/your/php bin/magento module:enable --clear-static-content Siphor_CustomAfter doing this and refreshing your Magento store, you might get encounter the following error.
Please upgrade your database: Run "bin/magento setup:upgrade" from the Magento root directory.
The following modules are outdated:
Siphor_Custom schema: current version - none, required version - 0.0.1
Siphor_Custom data: current version - none, required version - 0.0.1To rectify this, run the following command.
$ /path/to/your/php bin/magento setup:upgradeNow that the custom module has been registered, the module’s di.xml file can be added.
This is where the controller override will be specified. The key information resides in the <preference> node.
The for attribute value specifies the class you intend to override, and the type attribute specifies your custom class name.
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<config xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="urn:magento:framework:ObjectManager/etc/config.xsd">
<preference for="Magento\Cms\Controller\Index\Index" type="Siphor\Custom\Controller\Index\Index" />
</config>
Finally, the custom controller class can be added with the code that adds the success message.
<?php
namespace Siphor\Custom\Controller\Index;
class Index extends \Magento\Cms\Controller\Index\Index
{
public function execute($coreRoute = null)
{
$this->messageManager->addSuccessMessage('Success!');
return parent::execute($coreRoute);
}
}
If you then head to the home page of your Magento store, you’ll see the success message printed out.
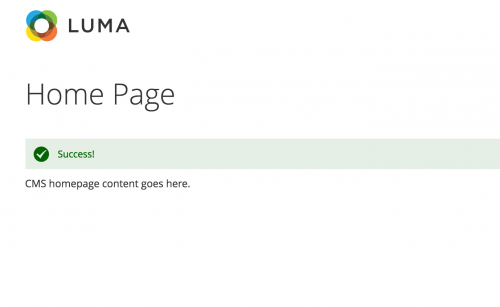
Although this is a basic example of how to rewrite an existing Magento 2 controller, the same steps apply to more complex controllers that need to be rewritten. When using this method, also check for any existing rewrites if there are any, to avoid rewrite conflicts.
It might be possible to rewrite a controller using Plugins, which give you the ability to extend functionality without creating rewrite conflicts. View the post for more information.
Note: This article is based on Magento Community/Open Source version 2.1.